Exocytosis and endocytosis definition 125680-Definition of endocytosis and exocytosis
Endocytosis of material into vesicles that move to oposite side of cell and fuse with plasma membrane, releasing material into extracellular space Collagen Family of closely related proteins which forms fibers with high tensile strength Definition of endocytosis Endocytosis, as opposed to exocytosis, refers to a key mechanism by which cells introduce large molecules, small cells, and extracellular particles These are encompassed in an invagination of the eukaryotic plasma membraneExocytosis is the process by which cells excrete waste and other large molecules from the cytoplasm to the cell exterior 49 and therefore is the opposite of endocytosis Exocytosis generates vesicles referred to as secretory or transport vesicles (Chapter 17)
1
Definition of endocytosis and exocytosis
Definition of endocytosis and exocytosis- Endocytosis and exocytosis mechanisms are forms of Active Transport, both using energy to transport particles in and out of the cell They both have different types similar in that they both transport materials across the cell membrane by forming vesicle poresLet's talk a little bit about exocytosis which is how the cell is able to release larger molecules that might be used by the rest of the body other cells or maybe it's going to be part of the extracellular matrix and to understand how this works is really the reverse of endocytosis we're going to go and produce some proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum this is our classic example those




Reciprocal Link Between Cell Biomechanics And Exocytosis Wang 18 Traffic Wiley Online Library
Exocytosis Exocytosis is the durable, energyusing process by which a cell directs the contents of secretory vesicles out of the cell membrane and into the extracellular space These membranebound vesicles contain soluble proteins to be secreted to the extracellular environment, as well as membrane proteins and lipids that are sent to become components of the cell membrane Endocytosis and exocytosis are the processes by which cells move materials into or out of the cell that are too large to directly pass through the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane Large molecules, microorganisms and waste products are some of the substances moved through the cell membrane via exocytosis and endocytosisEndocytosis is used for receptor signaling, nutrient uptake, membrane remodeling, pathogen entry, and neurotransmission, as well as modulation of cell signaling responses In developing tissues, endocytosis has been found to aid in cell migration Toxins, pathogens, and foreign debris have also been found to exploit different endocytic pathways
Exocytosis Definition Exocytosis is a type of process, in which involves the movement of materials from the inside of a cell to the exterior of the cell by the use of energy Exocytosis is a type of active transport because to perform this process energy is required It is a vital process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite Exocytosis works through a multistep process that is slightly different for regulated versus constituent endocytosis Regulated exocytosis occurs in five steps, while constitutive exocytosisExocytosis an active process in which vesicles containing excretory or secretory materials are actively carried to the periphery of the cell, and released to the outside when the vesicle membrane fuses with the cell membrane Compare ENDOCYTOSIS See PHAGOCYTOSIS, PINOCYTOSIS
Endocytosis and Exocytosis Describe the primary mechanisms by which cells import and export macromolecules In addition to moving small ions and molecules through the membrane, cells also need to remove and take in larger molecules and particles Exocytosis definition and purposes Exocytosis is the process by which cells move products from within the cell right into the extracellular fluid Exocytosis occurs as soon as a vesicle fuses v the plasma membrane, enabling its components to be released outside the cellExocytosis offer the following purposesInformation and translations of endocytosis in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web The process which is the opposite to endocytosis is exocytosis US National Library of Medicine (000 / 0 votes



What Is Exocyotosis And Endocytosis Quora



Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Venn Diagram Boyar
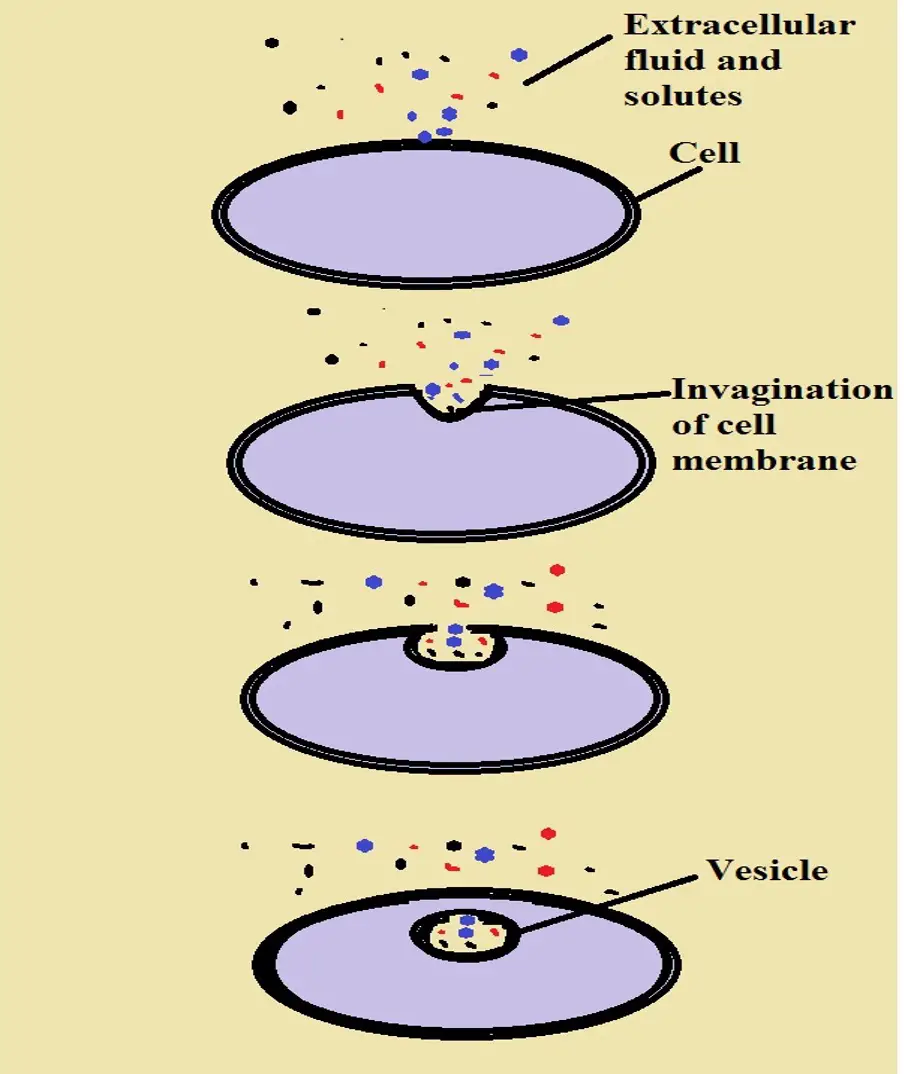
Definition of endocytosis in the Definitionsnet dictionary Meaning of endocytosis What does endocytosis mean?Exocytosis is defined as the transport and fusion of secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane and the extracellular space There are three exocytosis pathways that deliver vesicles to the plasma membrane Found in all cells, the constitutive secretory pathway operates continuously to deliver freshly synthesized membrane lipids and proteins, and soluble secretory proteins from Endocytosis is a cellular mechanism that allows a cell to internalise substances from its surroundings, such as proteins, electrolytes, fluids, microorganisms, and some macromolecules These compounds are broken down into smaller elements by a variety of operations, either for use by the cell or for waste The immune system's white blood cells are perhaps the most prevalent cells which make use of endocytosis




Exocytosis Active Transport Definition Examples Expii




Endocytosis Exocytosis Cie A Level Biology Revision Notes
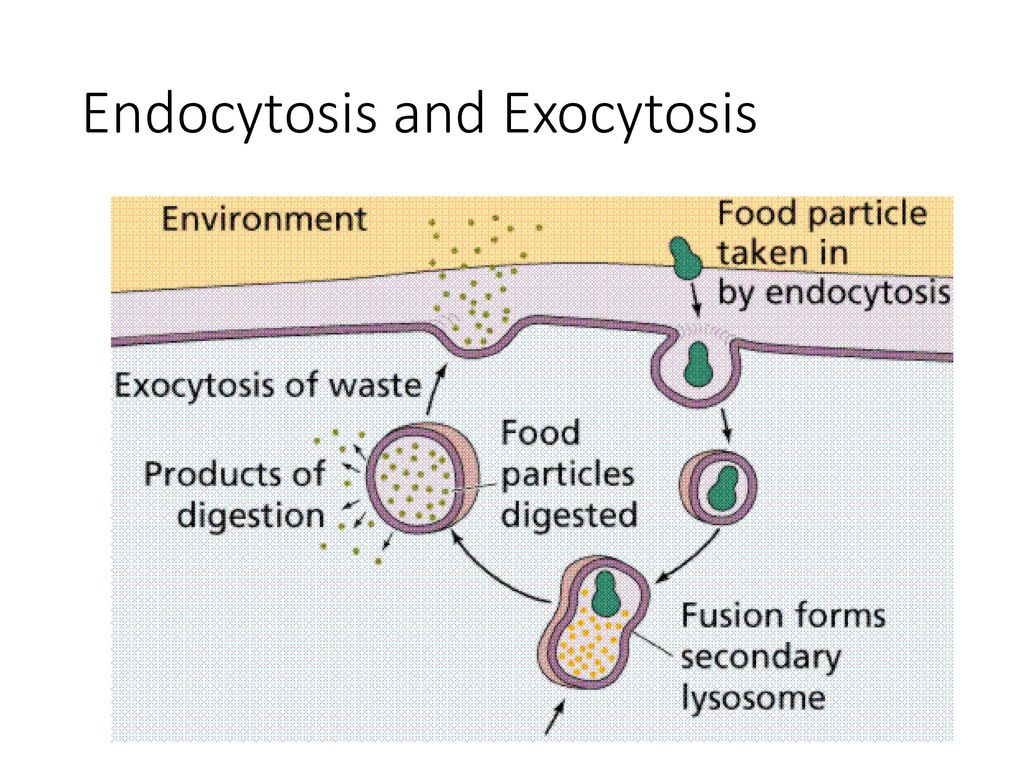
Most of the time, a body is processing endocytosis at one place, and exocytosis transpires at the other Endocytosis takes place when a foreign particle is to enter a cell through the selectively permeable cell membrane In contrast, exocytosis takes place when a vesicle formed gets out of the cell Chelsea RogersThe process by which substances areIt involves both endocytosis and exocytosis From one side of the cell, macromolecules enter the cell through endocytosis then travel across the cell and reach the other side of the cell Then through exocytosis, macromolecules exit the cell




Schematic Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Patterns Of Nanoparticles Download Scientific Diagram



3
Endocytosis Definition Endocytosis is the process by which a cell absorbs materials from the environment by engulfing and fusing them with its plasma membrane Etymology Greek éndon, which means "inside," Plus "kutos," which means "hollow vessel," Endocytosis is the process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment It is how cells get the nutrients they need to grow and develop Substances internalized by endocytosis include fluids, electrolytes, proteins, and other macromoleculesEndocytosis is also one of the means by which white blood cells of the immune As compared to endocytosis, exocytosis is a process that is used to transport materials from inside the cell to the external part of the cell by the use of energy Therefore, it is a type of active transport mechanism and it is the opposite of endocytosis Generally, in this mechanism of exocytosis, a special vesicle bound to the cell membrane, containing the cellular
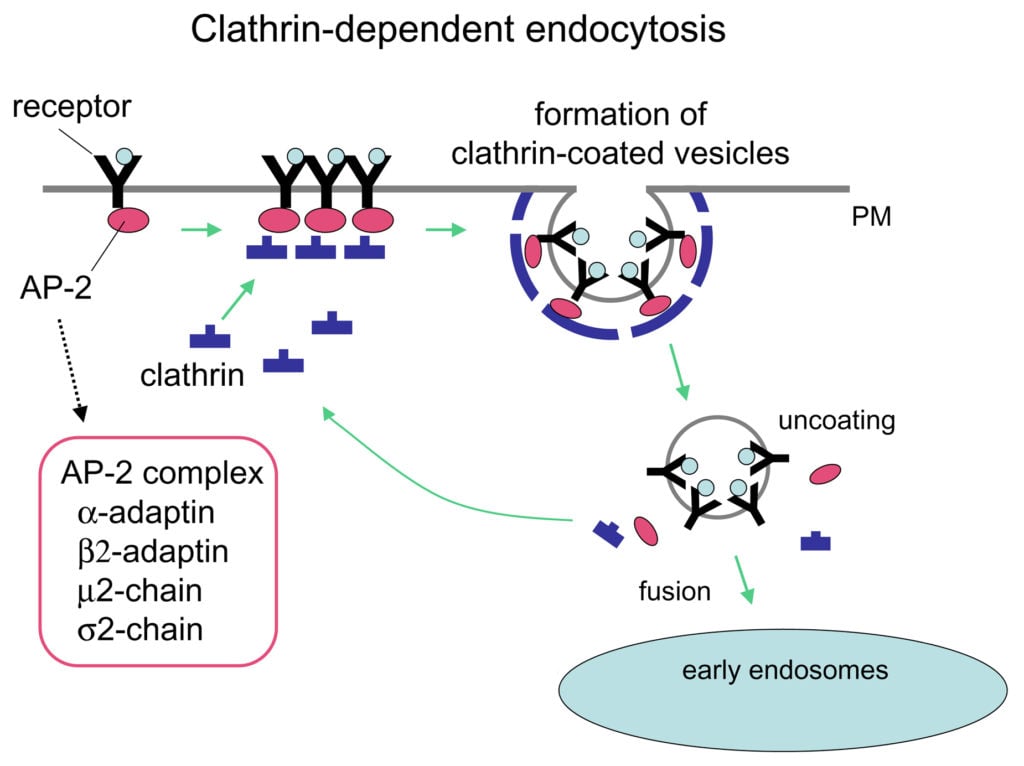



Endocytosis Definition Process And Types With Examples




Endocytosis Exocytosis Diagram Diagram Quizlet
Exocytosis is important in expulsion of waste materials out of the cell and in the secretion of cellular products such as digestive enzymes or hormones Endocytosis, on the other hand, is the process by which materials move into the cell There are three types of endocytosis phagocytosis, pinocytosis, and receptormediated endocytosisDefinition of exocytosis in English exocytosis noun Biology A process by which the contents of a cell vacuole are released to the exterior through fusion of the vacuole membrane with the cell membrane 'Membrane fusion is a key event in many essential cell processes, such as exocytosis, endocytosis, membrane recycling, protein sorting and Endocytosis and exocytosis are the names given to the active, bulk transport of products across the cell membraneThese processes allow larger molecules that cannot diffuse through the lipid bilayer to cross the membrane Endocytosis is the process by which substances are engulfed into the cellExocytosis is the reverse;
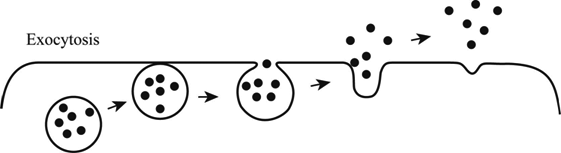



Definition Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Chegg Com
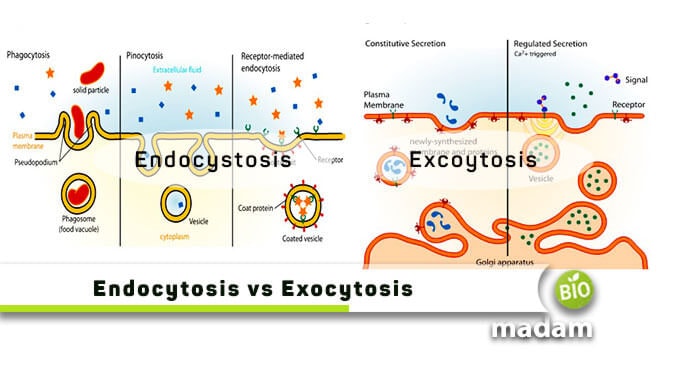



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biomadam
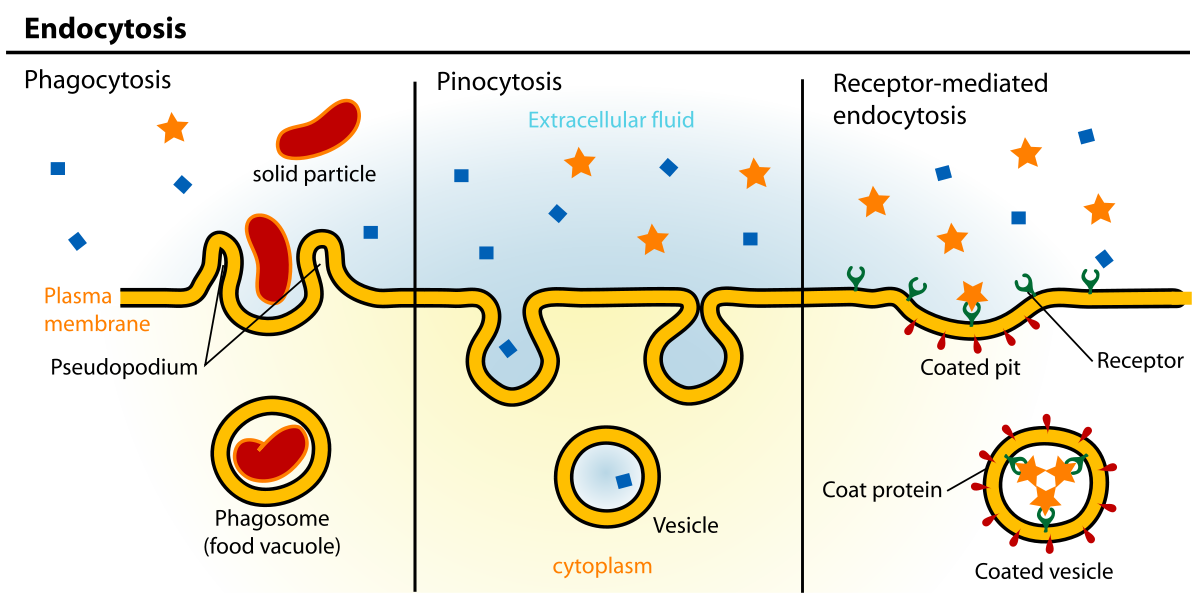
Exocytosis is the process of moving materials from within a cell to the exterior of the cell This process requires energy and is therefore a type of active transport Exocytosis, Exterior, Energy 2 Exocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosisReceptorMediated Endocytosis In contrast to phagocytosis, which plays only specialized roles, pinocytosis is common among eukaryotic cellsThe bestcharacterized form of this process is receptormediated endocytosis, which provides a mechanism for the selective uptake of specific macromolecules (Figure 1236)The macromolecules to be internalized first bind to specific cellExocytosis is an important process of plant and animal cells as it performs the opposite function of endocytosis In endocytosis, substances that are external to a cell are brought into the cell In exocytosis, membranebound vesicles containing cellular molecules are transported to the cell membrane The vesicles fuse with the cell membrane and expel their contents to the exterior




Exocytosis Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Venn Diagram Boyar
Endocytosis, recycling, and regulated exocytosis of glucose transporter 4 Biochemistry 11 Apr 19;50(15) doi /bi Epub 11 Mar 25 Authors Kevin Foley 1 , Shlomit Boguslavsky, Amira Klip Affiliation 1 Cell Biology Program, The Hospital forExocytosis definition, the transport of material out of a cell by means of a sac or vesicle that first engulfs the material and then is extruded through an opening in the cell membrane (distinguished from endocytosis) See more Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis is that The endocytosis is the transport of particles and substances inside the cell, while the exocytosis is intracellular transporting material outward Both processes are due to the need of the cell to maintain with its surroundings an exchange of materials for its survival




Pdf Endocytosis And Exocytosis Of Nanoparticles In Mammalian Cells Semantic Scholar




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Best One
Endocytosis is the process of actively transporting molecules into the cell by engulfing it with its membrane Endocytosis and exocytosis are used by all cells to transport molecules that cannot pass through the membrane passively Exocytosis provides the opposite function and pushes molecules out of the cell Endocytosis definition Endocytosis is a cellular process by which cells internalize substances from their external environment The term "Endocytosis" was first proposed by De Duve in 1963 Endocytosis is used by all eukaryotic cells to Exocytosis, as contrast to endocytosis, is a process that uses energy to transfer items from the inside of the cell to the outside of the cell As a result, it is an active transport system that is the polar opposite of endocytosis In this technique of exocytosis, a specific vesicle bound to the cell membrane that contains the cellular




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




Cbse Class 11 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Offered By Unacademy
Transport larger molecules such as proteins and polysaccharides, and even very large particles Click again to see term 👆 Tap again to see term 👆 Exocytosis Click card to see definition 👆 Tap card to see definition 👆 a process in which material inside a cell is packaged into vesicles and excreted into the extracellular mediumExocytosis ( exo = external, cytosis = transport mechanism) is a form of bulk transport in which materials are transported from the inside to the outside of the cell in membranebound vesicles that fuse with the plasma membrane Diagram illustrating the process of exocytosis Image modified from OpenStax Biology (original work by Mariana Ruiz Exocytosis is the natural process of transporting molecules from within a cell to the outside space In this process, the vesicles containing the fluid enclosed by a lipid bilayer fuse with the plasma membrane to release their contents outside the cell The term 'exocytosis' was proposed by De Duve in 1963 It occurs in all living cells




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Read Biology Ck 12 Foundation




Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Flashcards Quizlet
Exocytosis (/ ˌ ɛ k s oʊ s aɪ ˈ t oʊ s ɪ s /) is a form of active transport and bulk transport in which a cell transports molecules (eg, neurotransmitters and proteins) out of the cell (exo cytosis)As an active transport mechanism, exocytosis requires the use of energy to transport material Exocytosis and its counterpart, endocytosis, are used by all cells because most chemicalEndocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane and bringing it to cell But Exocytosis is the process of vesicles fusing with the plasma membrane and releasing their contents to the outside of the cell 21K views · In summary, endocytosis is the import of molecules and particles into the cell by folding the cell membrane inward to form vesicles There are four kinds of endocytosis




Solved 17 Contrast The Following Terms Exocytosis Chegg Com



What Is An Example Of Exocytosis Quora
Definition of Endocytosis Endocytosis is a cellular mechanism by which a cell internalizes substances such as proteins, fluids, electrolytes, microorganisms, and certain macromolecules from its external environment These substances are subjected to certain processes of decomposition into smaller elements, either for use by the cell or for elimination Endocytosis is of two types viz phagocytosis, also known as cellular eating and pinocytosis, also referred to as cellular drinking Exocytosis, on the other hand, is described as the process of fusing vesicles with the plasma membrane to release their contents to the external environment of the cell The basic difference between Exocytosis And Endocytosis is tabulated Diffusion & Osmosis Endocytosis & Exocytosis Active transport & Passive Transport Diffusion Similarities Diffusion is the process in which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration Similarities
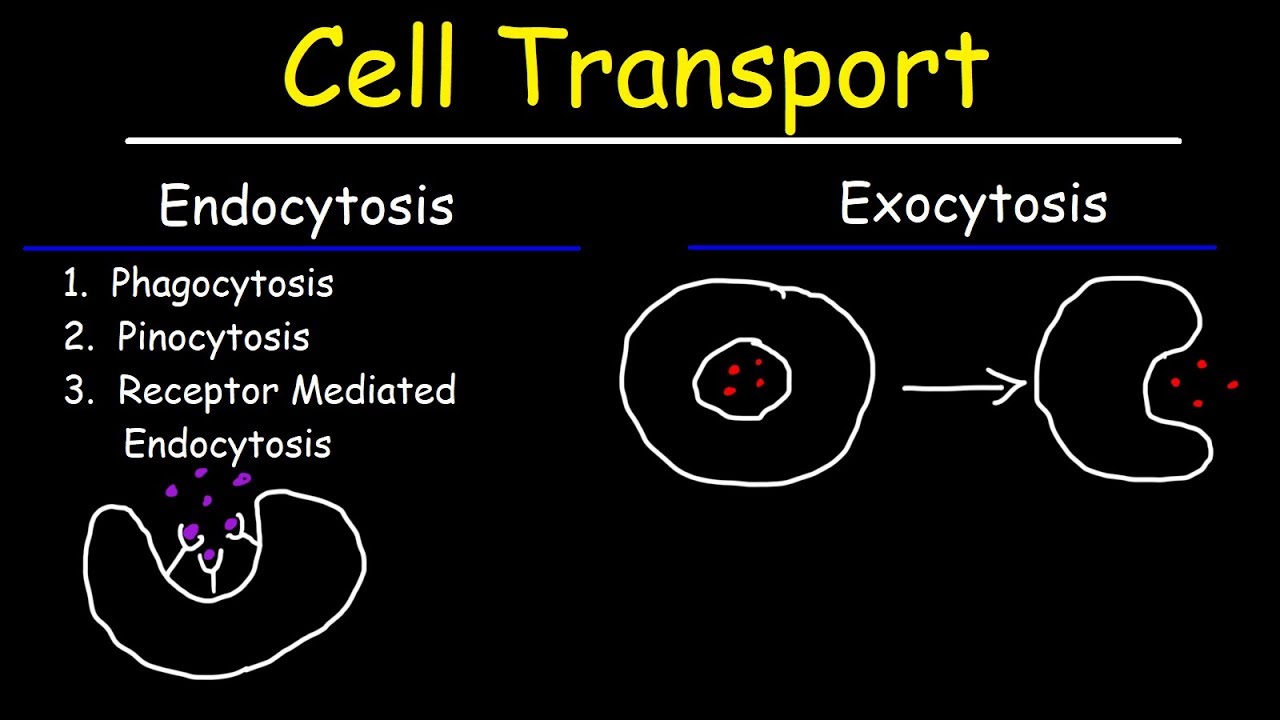



Cell Transport Endocytosis Exocytosis Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis Youtube



Plasma Membrane Cell Processes Part 3 Ppt Video Online Download
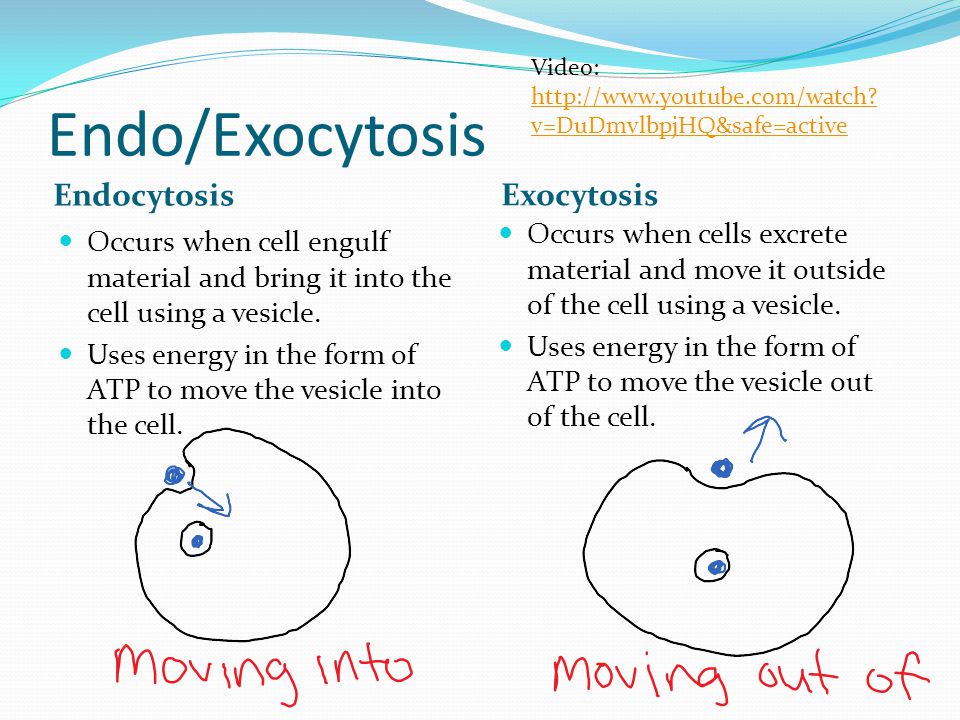
Endocytosis definition and purposes Endocytosis is the process by which cells take in substances from outside of the cell by engulfing them in a vesicle What is difference between endocytosis and exocytosis?Endocytosis is the process of capturing a substance or particle from outside the cell by engulfing it with the cell membrane, andTherefore, one of the biggest differences between endocytosis and exocytosis is the fact that whereas endocytosis is the process of important molecules/pathogen entering into the cell, exocytosis serves to remove material out of the cell



Endocytosis Wikipedia




Endocytosis Definition Types Expii
Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Differences Functions While both exocytosis and endocytosis are involved in the transport of bulk material, they serve different functions Whereas exocytosis involves the transportation of materials (proteins, lipids, etc) synthesized in the cell to the extracellular matrix of to the cell membrane, endocytosis involves the movement of material from the



Endocytosis Definition 3 Types Active Or Passive Vs Exocytosis



Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Venn Diagram Boyar
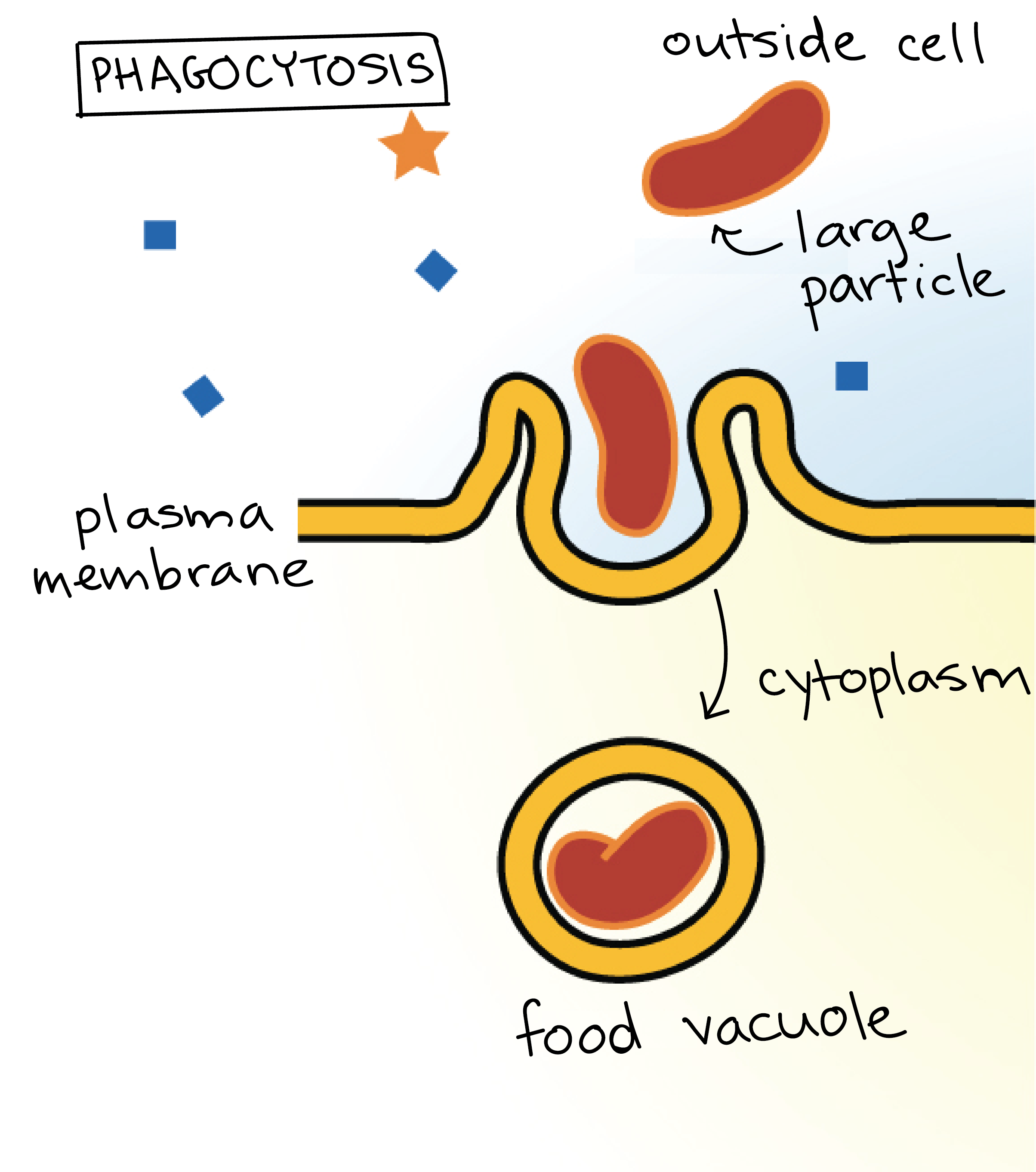



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Osmosis
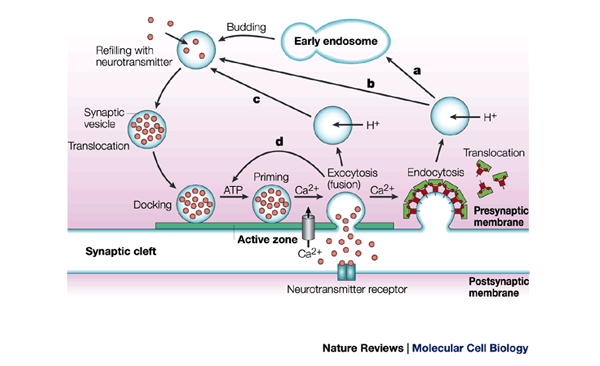



Temporal And Spatial Coordination Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I
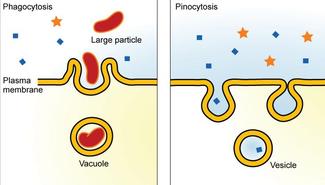



Cells Endocytosis Exocytosis Pathwayz



2 17 Exocytosis And Endocytosis Biology Libretexts



Endocytosis



Difference Between Endocytosis And Phagocytosis Pediaa Com




Endocytosis Exocytosis Autophagy Flashcards Quizlet



17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts




Reciprocal Link Between Cell Biomechanics And Exocytosis Wang 18 Traffic Wiley Online Library




Chapter 7 Exocytosis Endocytosis Flashcards Quizlet




Endocytosis Phagocytosis And Pinocytosis Video Khan Academy



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Interactive Diagram By Science With Mrs Lau




Active Transport The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Types Mechanism Function



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology
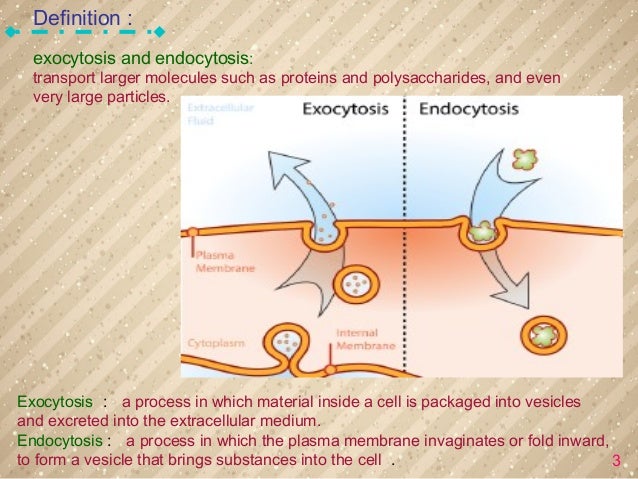



Exocytosis And Endocytosis Best One




What Is Exocytosis Mbinfo




Endocytosis Exocytosis By Matt Sargeant What Is Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Is A Process By Which Cells Absorb Molecules Such As Proteins Ppt Download



1




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Youtube
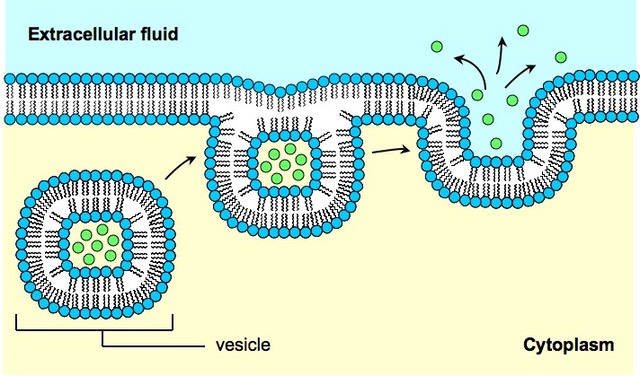



Bulk Transport Bioninja
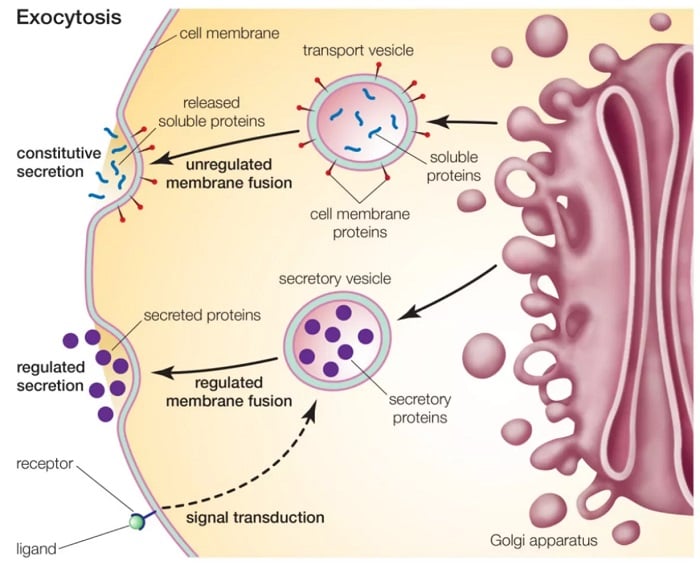



Exocytosis Definition Process And Types With Examples




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Best One




Endocytosis Definition Types Expii




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Across The Cell Membrane Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
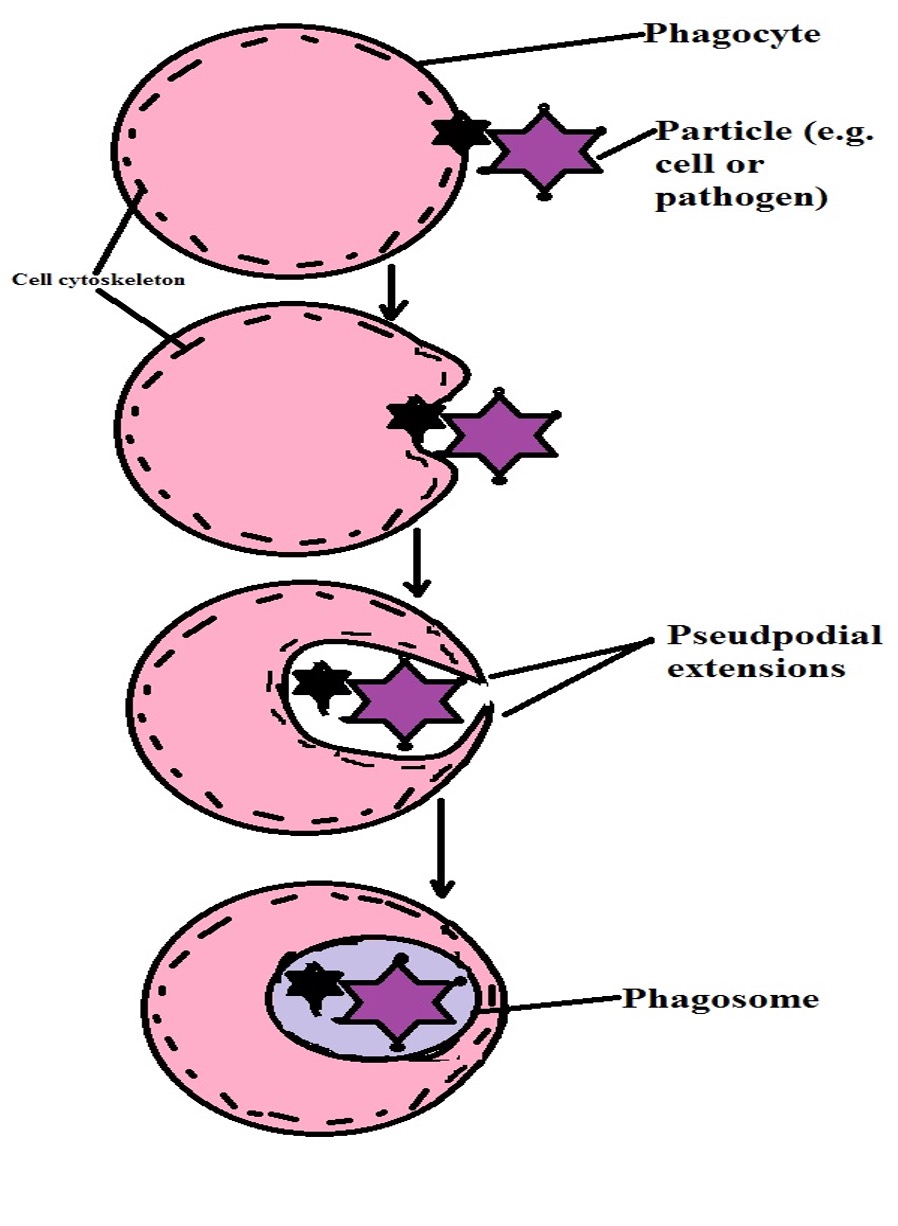



Endocytosis Definition 3 Types Active Or Passive Vs Exocytosis




Endocytosis Definition Types Examples Video Lesson Transcript Study Com




Plant Life Endocytosis And Exocytosis




Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Difference Between Endocytosis And Transcytosis Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms




Three Types Of Endocytosis Receptor Mediated Pinocytosis And Phagocytosis Human Anatomy And Physiology Science Notes Biochemistry




At The Intersection Of Exocytosis And Endocytosis In Plants Zhang 19 New Phytologist Wiley Online Library




Schematic Representation Of Sites Of Exocytosis Or Endocytosis In Download Scientific Diagram




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Across The Cell Membrane Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
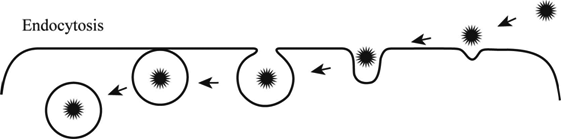



Definition Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Chegg Com
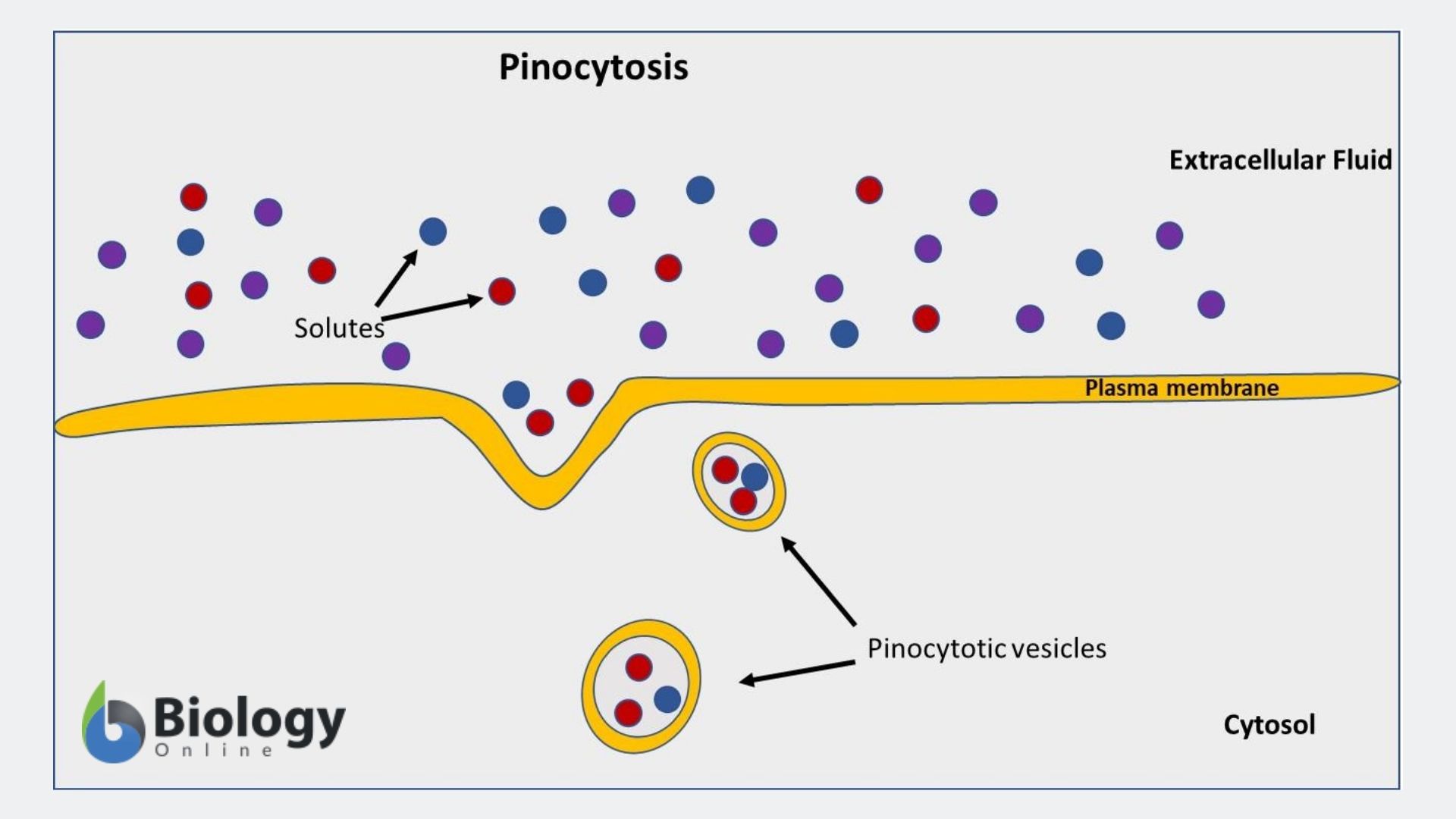



Pinocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary



17 4 Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology Libretexts



Difference Between Exocytosis And Endocytosis Difference Between




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks



1



Exocytosis And Endocytosis
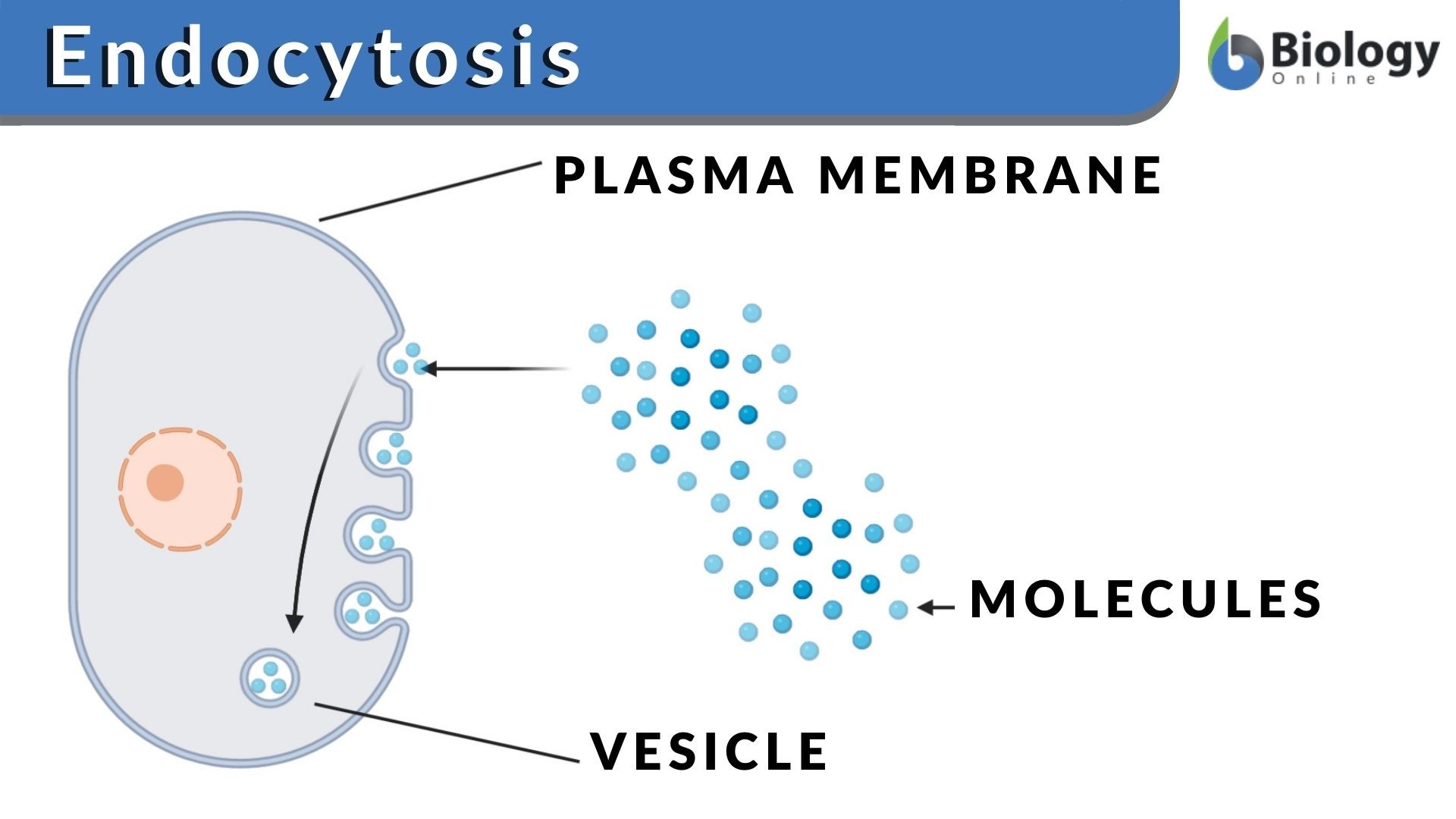



Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary



Exocytosis And Endocytosis
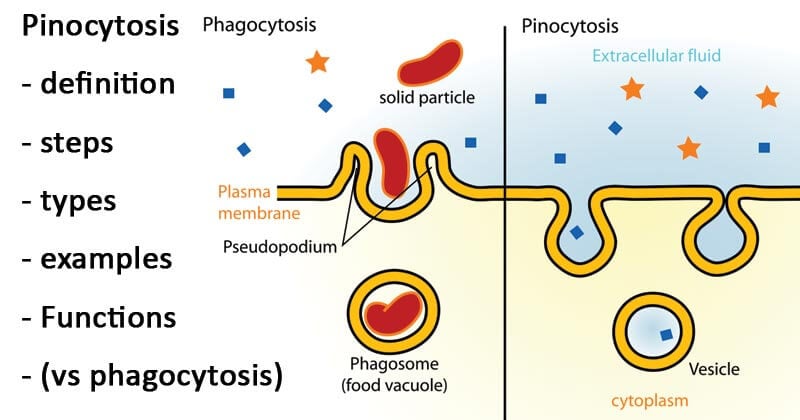



Pinocytosis Definition Steps Types Examples Vs Phagocytosis




Learn About Forms Of Endocytosis Chegg Com
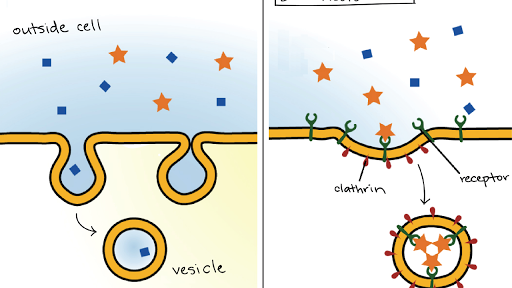



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy




Calcium Independent Exo Endocytosis Coupling At Small Central Synapses Sciencedirect
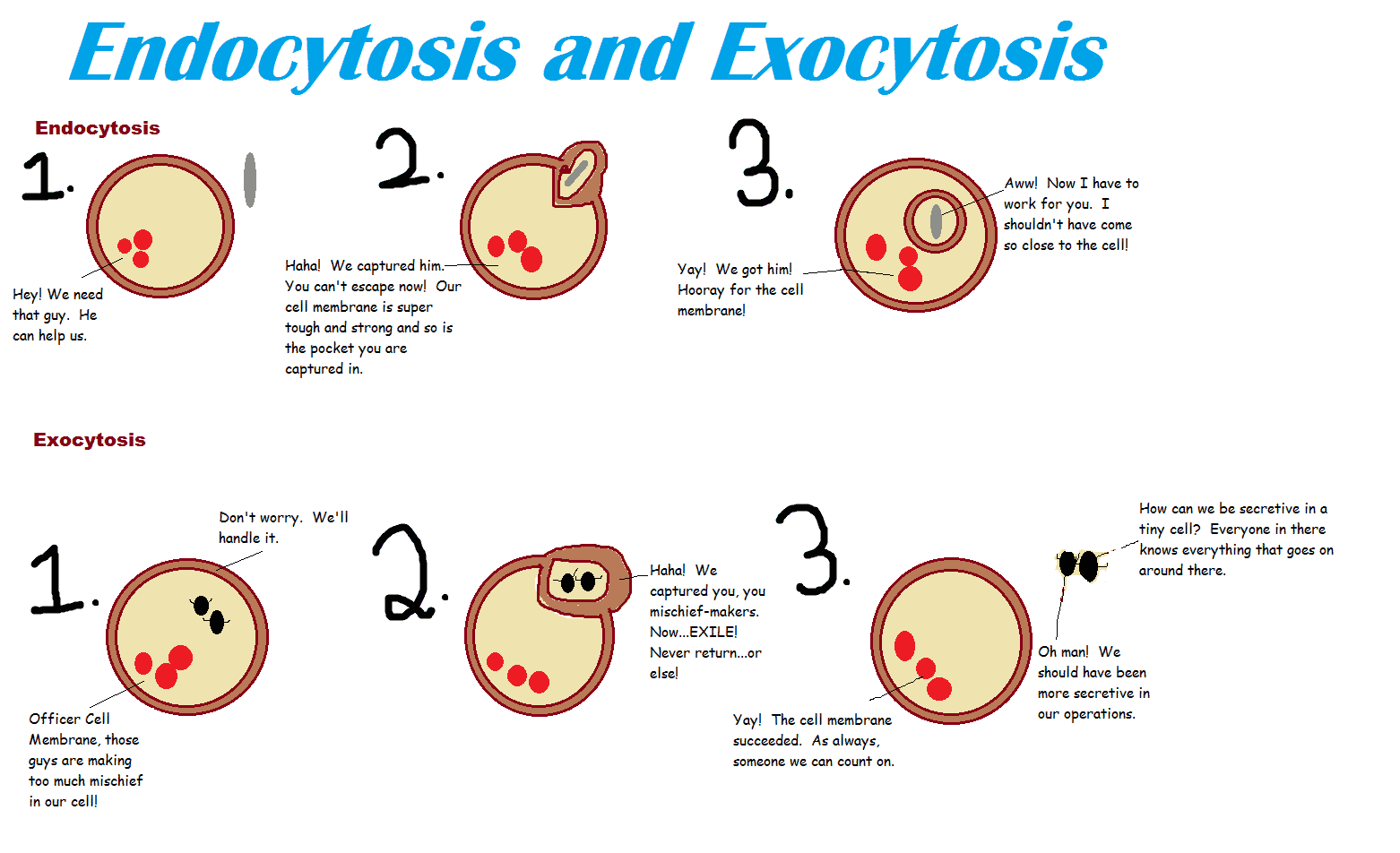



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis




Exocytosis Wikipedia




Endocytosis Biology Britannica




Learn About Exocytosis And Endocytosis Chegg Com



Difference Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Read Biology




Endocytosis And Exocytosis In Urdu Definition Of Endocytosis Biology With Tahira Yasmeen Youtube




What Is Membrane Trafficking Mbinfo
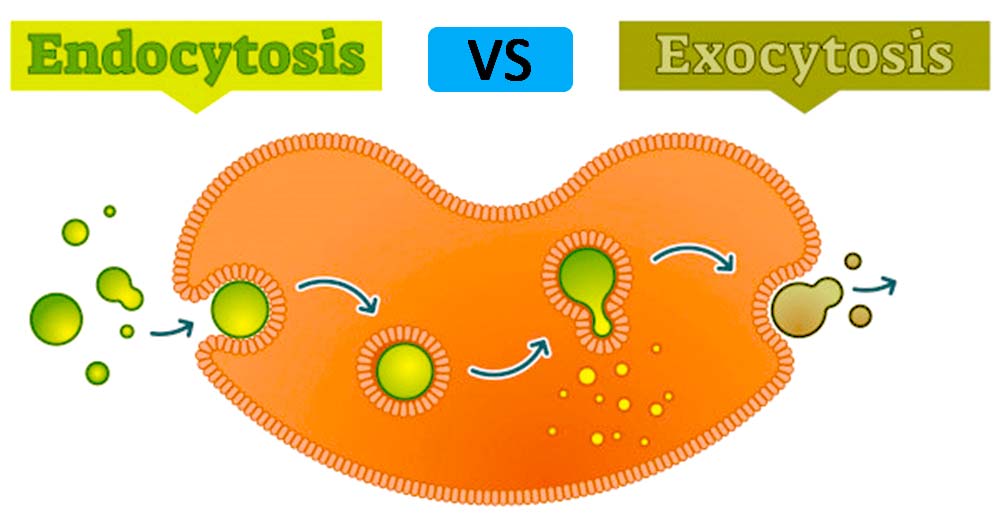



Endocytosis And Exocytosis Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Biology For Majors I




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Differences And Similarities Technology Networks




Plant Life Endocytosis And Exocytosis
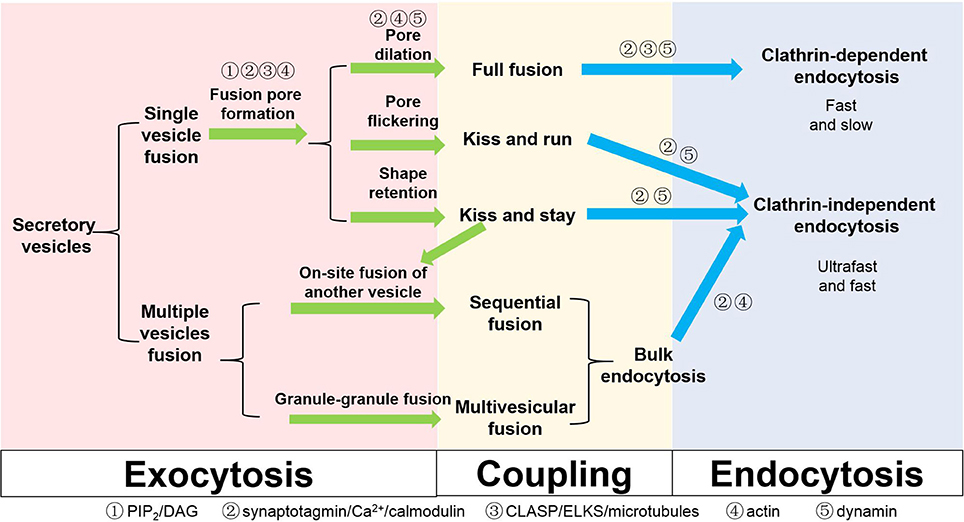



Frontiers Exocytosis Endocytosis And Their Coupling In Excitable Cells Molecular Neuroscience




Endocytosis Exocytosis Infographics Google Search Biologia
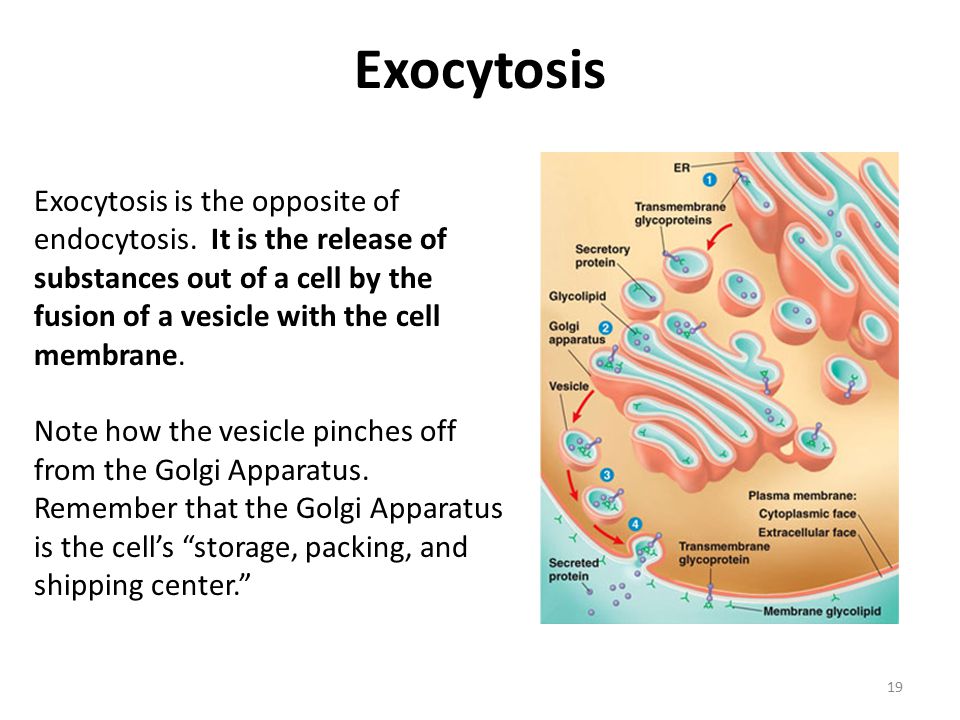



Active Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Ppt Download




Exocytosis And Endocytosis Flashcards Quizlet




Active Transport Biology I




Neuronal Exocytosis Sciencedirect
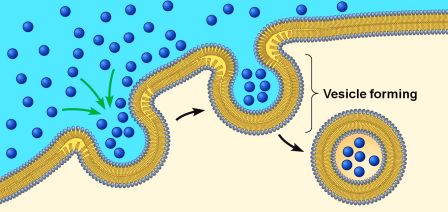



What Is The Relationship Between Endocytosis And Exocytosis Socratic




Ib Biology 1 4 Slides Cell Transport




Endocytosis And Exocytosis Simple Explaination In Hindi Bhushan Science Youtube




Exocytosis Examples Triggers What Is Exocytosis Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/exocytosis_2-5ae36dab04d1cf003cef3c48.jpg)



A Definition Of Exocytosis With Steps And Examples




Endocytosis Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary
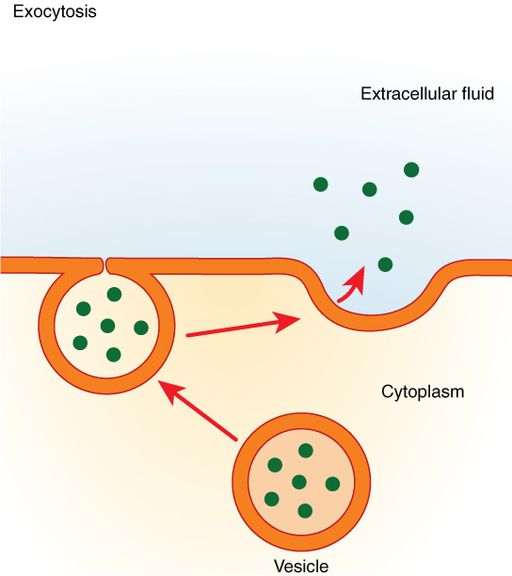



Endocytosis Vs Exocytosis Definitions Types Of Exocytosis
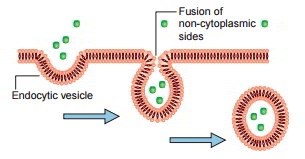



Vesicular Transport Endocytosis And Exocytosis Earth S Lab
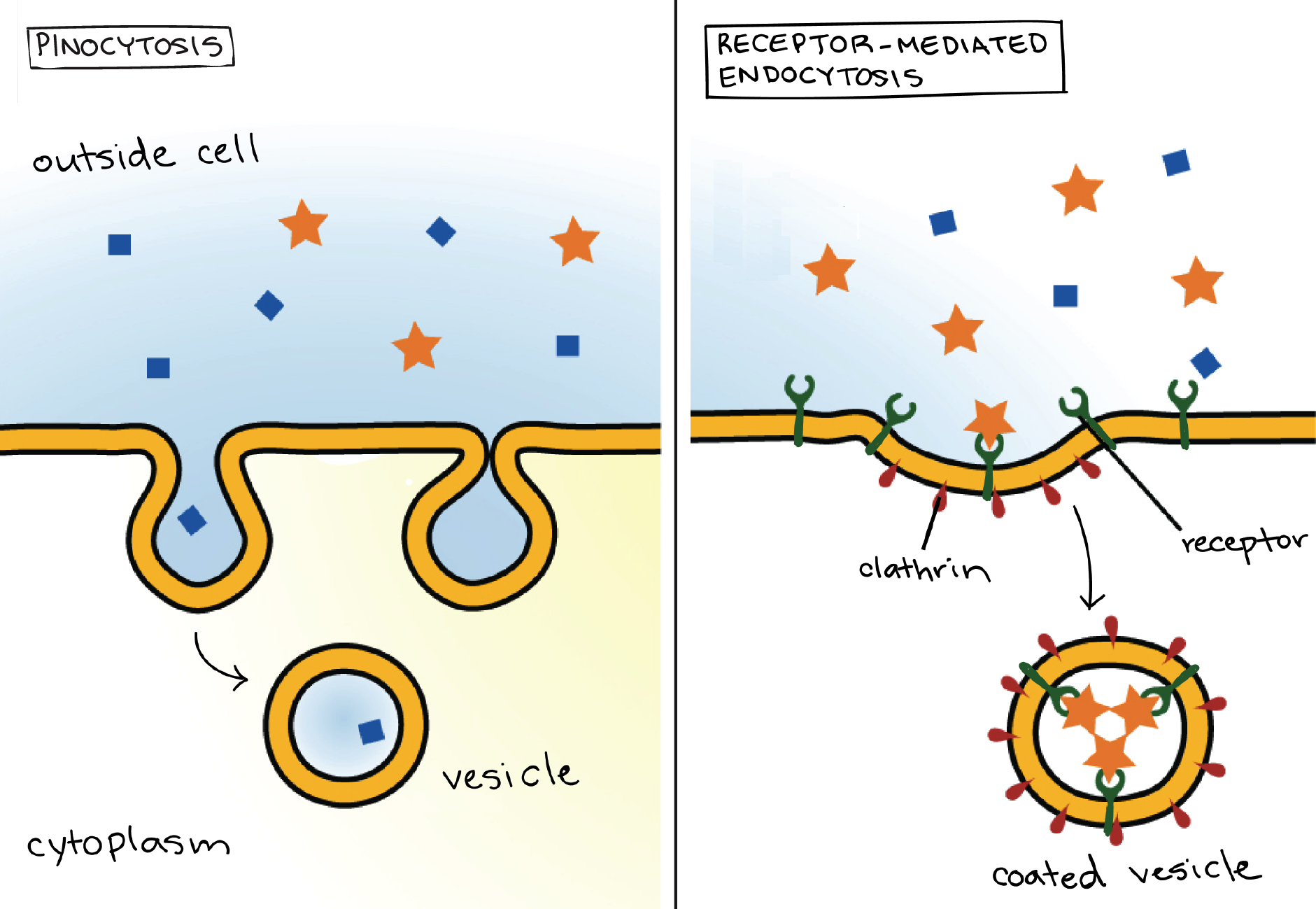



Bulk Transport Article Khan Academy
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/endocytosis-5ad64d57c0647100386364bb.jpg)



A Definition Of Endocytosis With Steps And Types



What Is The Definition Of Endocytosis And Exocytosis Quora
コメント
コメントを投稿